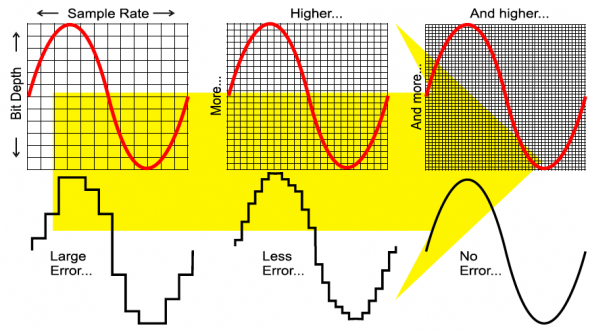
The audio bit depth determines the number of possible amplitudes values we can record for each sample. The most common are 16-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit. Each is a binary term, representing the number of possible values.
- 16-bit: 65,536 values
- 24-bit: 16,777,216 values
- 32-bit: 4,294,967,296 values
With a higher audio bit depth, more amplitudes values are available and thus a higher resolution. therefore a digital approximation of the amplitude becomes closer to the original fluid analog wave. Increasing the audio bit depth along with the sample rate creates more total points to reconstruct the analog wave.
The fluid analog wave does not always perfectly line up with the possible bit value, regardless of the resolution. As a result, the last bit of the data denoting the amplitude is rounded to either 0 or 1, in a process called quantization. This means there are essentially randomized parts of the signal. In digital audio, we hear this as white noise, which we call the noise floor. Digital quantization error introduces noise into our audio.
Harmonic relationships between the sample rate and audio, along with the bit depth, can cause certain patterns in quantization. This is known as correlated noise, which we hear as resonances in the noise floor at certain frequencies. However, we can perform artificial randomization to make sure their patterns don’t occur. In a process called dithering, we can randomize how this last bit gets rounded.
The amplitude of the noise floor becomes the bottom of our possible dynamic range. On the other side of the spectrum, a digital system can distort if the amplitude is too high when a signal exceeds the maximum value the binary system can create. This level is referred to as 0 dBFS.
The bit depth determines the number of possible amplitude values between the noise floor and 0 dBFS.
Can you hear the difference between audio bit depths? In HIFI we commonly see 16-bit and 24-bit, the noise floor of 16 bit is so incredibly low that it has no audible difference than 24-bit. But 24-bit can have some benefits due to anti-aliasing and other technical reasons. Anything higher than 24-bit is pointless.
*Image and info by izotope